Systems Thinking
The development of systems thinking took off with the landmark book General Systems Theory (Ludwig von Bertalanffy, 1 januari 1969) written by Ludwig von Bertalanffy. The goal was to develop an all-encompassing systems theory to serve as a basis for interdisciplinary research. Systems thinking is the ability to understand and intervene in complex systems. A system is comprised of elements, which can also be called parts, entities, persons, and components. The elements are interconnected, i.e., they are related to each other. The crucial aspect of systems thinking is the necessity to understand a system’s behavior as a whole. The behavior cannot be deduced from its constituting elements alone. It is because of the element’s interconnectedness that new properties emerge. This is reflected in the famous quote about systems thinking.
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
To illustrate this quote, take for example an aircraft. It is a complex system having many parts such as fuselage, wings, engines, and landing gear. When these parts are assembled in the right way, the desirable property of being able to fly emerges. The parts in itself do not have this emergent property, that is, an engine and the other parts as well cannot fly on their own.
System Conception
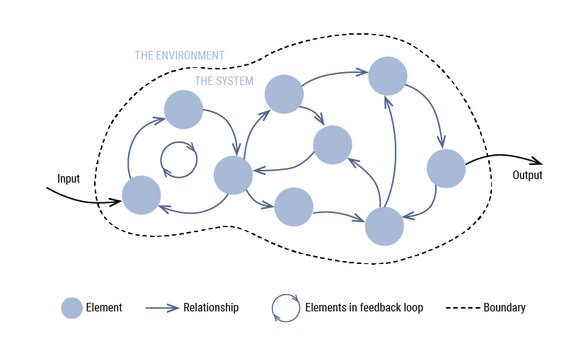
In the original conception of systems thinking, now called the hard systems approach or first-order cybernetics, a system has a purpose reflected in transforming some input to some output as depicted in the figure below. A system has a boundary, which separates the system from its environment. Which elements are regarded as inside the system, and which are not, is largely a matter of what is considered the system’s purpose. For instance, is a pilot part of the aircraft system or not? The answer is of course, that depends. It depends on the purpose of investigating the aircraft system. On the one hand, if the purpose is simply to investigate the flying characteristics of the aircraft, then the pilot is not necessarily part of the system, instead he is part of the environment. On the other hand, if the purpose is an inquiry into transportation of goods and persons, then the pilot is part of the system because of his crucial role to steer and navigate the aircraft. (Perhaps in the future we can replace a pilot by a subsystem comprised of AI algorithms, but this is really replacing one (human) subsystem for a computerized one.)
Systems thinking is an anti-reductionism approach, which makes it different from more traditional research approaches that study elements in isolation. The reasoning goes if all the elements are understood in isolation, then the whole is understood as well. Systems thinking takes the interconnectedness between elements into account. This has far reaching consequences because due to the interconnectedness the difference between cause and effect becomes obscured. An element may have an effect on another element, which on its turn have an effect on yet another element, and eventually may have an effect on the first element that seems to have started the cause of events in the first place. But due to this circularity, it is impossible to pinpoint the exact element that really caused a particular effect, because there really isn’t one.
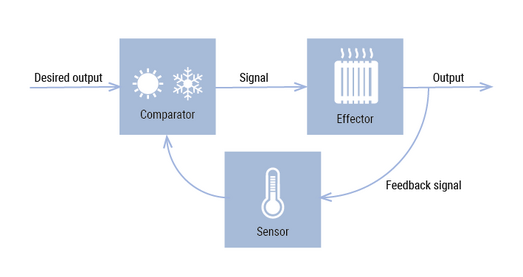
Systems thinking assumes reflexive domains, meaning that elements are part of the same domain and act and react on each other. First-order cybernetics studied the nature of these feedback loops in great detail. In particular, the role of negative feedback was investigated. A well-known example is the thermostat that keeps the temperature in a room between preset limits. If the temperature is too low, the heater, or more formally, the effector, is turned on. If it is too high, the heater is turned off. So, the real, measured temperature is fed back to a control unit that calculates the difference, hence the phrase negative feedback, between the desired and measured temperature. The difference in temperature is then used to steer the heater.
Statement: A system as a whole is comprised of parts. Systems thinking is about understanding the interactions between the parts.
Taming Complexity
A system consists of elements and relations. The number of elements and relations to consider tend to become quite large for complex systems. To tame the complexity, there are basically two options to consider, and these two options can be combined.
The first option is to decompose a system into a number of sub-systems, and sub-systems can in their turn be decomposed as well, and so on. Each sub-system has a boundary to separate it from its environment. Therefore, sibling sub-systems are part of a sub-system’s environment. As a rule of thumb, a sub-system should contain 7 ± 2 elements. The “7 ± 2” rule stems from Miller (Miller, G. A., 1 januari 1956) who studied the limits of human capacity to process information. In principle, the number of objects an average human can hold in short-term memory is 7 ± 2. However, limiting the number of elements in sub-systems is not sufficient for reducing complexity. The “strong cohesion – low coupling” rule should be applied as well. This rule states that the elements in a sub-system should cohere in the sense that they belong together and have strong ties, whereas the coupling with elements residing in other sub-systems should be kept to a minimum. In this way, it is easier to comprehend a sub-systems behavior, and if needed, to adapt it with minimal effects on other sub-systems.
The second option is to reduce the number of aspects to consider. The system elements are interconnected with all kinds of relations. By taking only a few aspects into account, the complexity of a system can be reduced. For instance, if we want to look at the world from a financial point of view, a financial system can be devised that considers cash flow between elements only. A system conceived this way is called an aspect-system.
The division of a system in sub-systems and aspect-systems are abstraction mechanisms to ignore irrelevant details that obscure rather than reveal a system’s behavior from a particular point of view. It should be kept in mind, however, that the very idea of systems thinking is its anti-reductionism stance. A system can only be understood in how the parts relate to the whole, and vice versa. Nevertheless, sub-systems and aspect-systems do help in taming complexity, but the whole should not get out of sight.
Developments
It is important to note that second-order cybernetics eventually reached another system concept in which the notion of purpose and input-output transformation was replaced by the concept of self-observing and self-producing systems. These are systems that reproduce themselves from their own elements, which is the case for all living organisms. The purpose of a system is then simply to reproduce. Also, the hard systems approach evolved in soft and critical systems approaches in which the opinions of the stakeholders are taken into account. But these two approaches retained essentially the original system concept of purpose and input-output transformation.
In this book, besides second-order cybernetics, the traditional hard, soft and critical systems thinking approaches are discussed. The latter three are named as the first, second, and third wave, respectively. A fourth wave is emerging, which is called DSRP Theory. DSRP stands for Distinctions, Systems, Relationships, Perspectives. Although DSRP theory is not discussed here, for interested readers, its uniting concepts are worth exploring.
The current state of affairs in systems thinking is collected in the two following books: Systems Approaches to Managing Change: A Practical Guide, recently updated in a second edition (Martin Reynolds and Sue Holwell, 1 maart 2020), and Critical Systems Thinking and the Management of Complexity (Michael C. Jackson, 1 maart 2019). These two books cover a lot of ground, including complexity theory and the essentials of design thinking.