LC 00885: verschil tussen versies
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
||
| Regel 11: | Regel 11: | ||
7. Possibilities for aquaculture (Abbenis, 2018) | 7. Possibilities for aquaculture (Abbenis, 2018) | ||
==== Limits and opportunities ==== | ==== Limits and opportunities ==== | ||
The possibilities for Schorerpolder are limited because of its location, what is to be found below and above the surface and where it is used for. The layer approach was used to define the spatial impact of the area. The most important outcome was | The possibilities for Schorerpolder are limited because of its location, what is to be found below and above the surface and where it is currently used for. The layer approach was used to define the spatial impact of the area. The most important outcome of the research was the amount of cables and tubes that where present in the area, all of importance to the harbor (Lambregts, 2018). | ||
[[Bestand:4 alternative designs.jpg|miniatuur|Four alternative designs for Schorerpolder.]] | |||
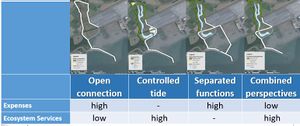
==== Designs ==== | |||
The four different designs of Schorerpolder, were assessed based on the ecosystem services and expenses on creation and maintenance. | |||
Open connection: Opening up the polder completely would allow for natural processes that make intertidal areas so unique to shape and form the area. By letting these tides flow through the area unhindered the potential intertidal area is maximized which is beneficial for wading birds but downside is that all dikes would have to be overhauled. | |||
Controlled tide: This design needs less changes in the primary dike than the previous one and is beneficial as fish nursery (e.g. eel) because of the presence of a gully and denitrification can occur in anaerobic environments. In addition salt marshes can develop more easily and can store CO2. | |||
Separated functions: | |||
{{Light Context | {{Light Context | ||
|Supercontext=PR 00190 | |Supercontext=PR 00190 | ||
Versie van 6 aug 2018 09:43
Start project
On the first of February 2018, the project started to map different alternative designs based on previous studies and outcomes of new studies. Two researchers of the Building with Nature group of HZ coordinated this research and guided the involved students. The expertise of researchers of water safety and spatial planning, civil engineering and vitality and tourism was added. A stakeholder meeting was organised the 14th of June to share the outcomes of the first six months and to organize discussion about the different alternative designs.
Ecosystem services
Groups of students compared the alternative designs for ecosystem services 1. Sustainable use of abiotic resources (Sinke et al. 2018) 2. Use as a nursery for fish (Lee et al. 2018) 3. Provision of habitat and foraging area for birds (Burger et al. 2018) 4. Enhance the biodiversity of hard structures in the intertidal zone of the area (Metekohij et al. 2018) 5. Quantification of primary production and carbon dioxide sequestration (Mol et al. 2018) 6. Quantification of the water purification capacity of salt marshes (Correa et al. 2018) 7. Possibilities for aquaculture (Abbenis, 2018)
Limits and opportunities
The possibilities for Schorerpolder are limited because of its location, what is to be found below and above the surface and where it is currently used for. The layer approach was used to define the spatial impact of the area. The most important outcome of the research was the amount of cables and tubes that where present in the area, all of importance to the harbor (Lambregts, 2018).
Designs
The four different designs of Schorerpolder, were assessed based on the ecosystem services and expenses on creation and maintenance. Open connection: Opening up the polder completely would allow for natural processes that make intertidal areas so unique to shape and form the area. By letting these tides flow through the area unhindered the potential intertidal area is maximized which is beneficial for wading birds but downside is that all dikes would have to be overhauled. Controlled tide: This design needs less changes in the primary dike than the previous one and is beneficial as fish nursery (e.g. eel) because of the presence of a gully and denitrification can occur in anaerobic environments. In addition salt marshes can develop more easily and can store CO2. Separated functions: