Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
||
| Regel 3: | Regel 3: | ||
==== References ==== | ==== References ==== | ||
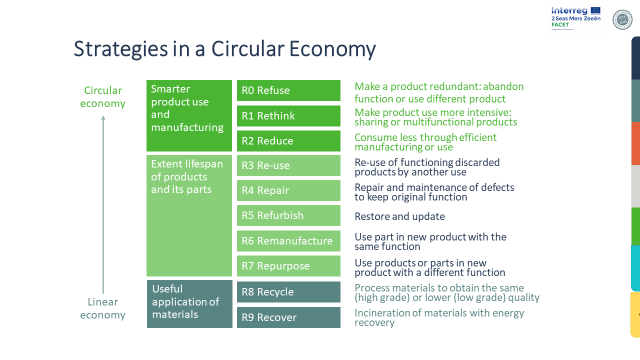
[1] Figure: Potting, José, et al. Circular economy: measuring innovation in the product chain. No. 2544. PBL Publishers, 2017. | [1] Figure: Potting, José, et al. Circular economy: measuring innovation in the product chain. No. 2544. PBL Publishers, 2017. | ||
{{Project FACET Tool config}} | {{Project FACET Tool config}} | ||
{{Project | {{Project | ||
|Name=Strategies in a Circular Economy | |Name=Strategies in a Circular Economy | ||
|Start date=18/03/2021 | |Start date=18/03/2021 | ||
|Summary=There exists a hierarchy of circularity strategies, different levels to reduce the consumption of natural resources and materials, and minimize the production of waste[1]. They can be ordered for priority according to their levels of circularity | |Summary=There exists a hierarchy of circularity strategies, different levels to reduce the consumption of natural resources and materials, and minimize the production of waste [1]. They can be ordered for priority according to their levels of circularity | ||
|Supercontext=PR 00275 | |Supercontext=PR 00275 | ||
|Topcontext=PR 00319 | |Topcontext=PR 00319 | ||
Versie van 18 mrt 2021 17:07
The R strategies are ranked from high circularity (low R - number) to low circularity (high R-number). [1].
References
[1] Figure: Potting, José, et al. Circular economy: measuring innovation in the product chain. No. 2544. PBL Publishers, 2017.