LC 00570: verschil tussen versies
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
||
| (5 tussenliggende versies door 2 gebruikers niet weergegeven) | |||
| Regel 1: | Regel 1: | ||
We make decisions based on past experiences, which is summarized in a LoF expression as | |||
<math>\overline{\underline{\overline{_{\lfloor}system|}environment}\Big|}</math> | |||
or in a similar vein as | or in a similar vein as | ||
<math>\overline{\underline{\overline{_{|}I|}world}\Big|}</math> | |||
The form expression is re-entered in its own indicational space in order to base a next step on past experiences. In the human cognition behavior model, this is modeled in the form of a PDCA-cycle in which the reflection activity corresponds with Check-Act/Adjust. But how precisely the past is taken into account is left implicit in the model. The precise details are usually not needed to get the message across. However, for precise modeling, e.g., for simulation purposes, the details do matter. The principles are worked out here in a rough sketch. | The form expression is re-entered in its own indicational space in order to base a next step on past experiences. In the human cognition behavior model, this is modeled in the form of a PDCA-cycle in which the reflection activity corresponds with Check-Act/Adjust. But how precisely the past is taken into account is left implicit in the model. The precise details are usually not needed to get the message across. However, for precise modeling, e.g., for simulation purposes, the details do matter. The principles are worked out here in a rough sketch. | ||
| Regel 10: | Regel 12: | ||
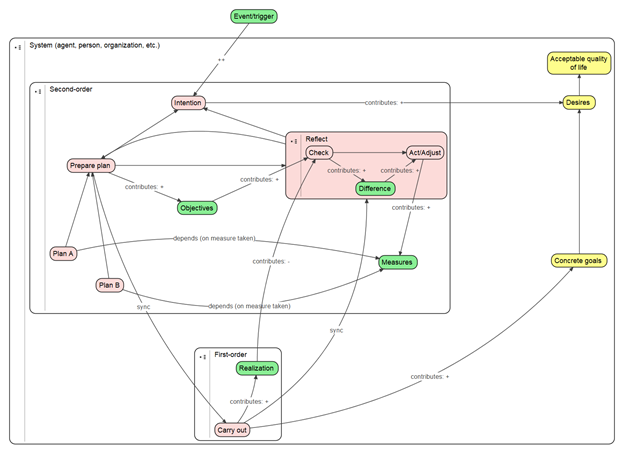
The system (agent, person, organization, etc.) is split in two roles: first-order role for carrying out the work, and second-order role for planning and monitoring. The objectives and the realization thereof is checked resulting in a difference. The difference then provides the input for determining the measures to be taken. In the next planning phase, either plan A or B is chosen dependent on the measures taken. In the section on EM<sub>ont</sub> executable model it is shown how the depends relation is refined to define precisely when a depends relation is satisfied or not. | The system (agent, person, organization, etc.) is split in two roles: first-order role for carrying out the work, and second-order role for planning and monitoring. The objectives and the realization thereof is checked resulting in a difference. The difference then provides the input for determining the measures to be taken. In the next planning phase, either plan A or B is chosen dependent on the measures taken. In the section on EM<sub>ont</sub> executable model it is shown how the depends relation is refined to define precisely when a depends relation is satisfied or not. | ||
So, history is taken into account by means of basing a next step on a past realization. The basic scheme can be further extended by incorporating practices and traces in the reflection activity. | So, history is taken into account by means of basing a next step on a past realization. The basic scheme can be further extended by incorporating practices and traces in the reflection activity. The reader is referred to {{Internal link|link=LC 00437|name=Practices and Traces|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}} for an elaborated discussion. | ||
{{LC Book config}} | {{LC Book config}} | ||
{{Light Context | {{Light Context | ||
| Regel 21: | Regel 23: | ||
|Context type=Situation | |Context type=Situation | ||
|Heading=Taking History into Account | |Heading=Taking History into Account | ||
|Show referred by=Nee | |||
|Show edit button=Ja | |Show edit button=Ja | ||
|Show VE button=Ja | |Show VE button=Ja | ||
|Show title=Ja | |Show title=Ja | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{LC Book additional | {{LC Book additional | ||
|Preparatory reading= | |Preparatory reading=LC 00569 | ||
}} | }} | ||
Huidige versie van 29 jun 2022 om 20:23
We make decisions based on past experiences, which is summarized in a LoF expression as
[math]\displaystyle{ \overline{\underline{\overline{_{\lfloor}system|}environment}\Big|} }[/math]
or in a similar vein as
[math]\displaystyle{ \overline{\underline{\overline{_{|}I|}world}\Big|} }[/math]
The form expression is re-entered in its own indicational space in order to base a next step on past experiences. In the human cognition behavior model, this is modeled in the form of a PDCA-cycle in which the reflection activity corresponds with Check-Act/Adjust. But how precisely the past is taken into account is left implicit in the model. The precise details are usually not needed to get the message across. However, for precise modeling, e.g., for simulation purposes, the details do matter. The principles are worked out here in a rough sketch.
The system (agent, person, organization, etc.) is split in two roles: first-order role for carrying out the work, and second-order role for planning and monitoring. The objectives and the realization thereof is checked resulting in a difference. The difference then provides the input for determining the measures to be taken. In the next planning phase, either plan A or B is chosen dependent on the measures taken. In the section on EMont executable model it is shown how the depends relation is refined to define precisely when a depends relation is satisfied or not.
So, history is taken into account by means of basing a next step on a past realization. The basic scheme can be further extended by incorporating practices and traces in the reflection activity. The reader is referred to Practices and Traces for an elaborated discussion.