Implementation process
y looking at the the activities, actors and methods or approaches used, this section will provide a better understanding of the implementation process of the MLS approach. We will describe the point of departure, who was involved (when, why and how) and what key decisions were made when and why.
Point of departure of FRM strategies
Assens has been working on flood protection at the harbour areas.
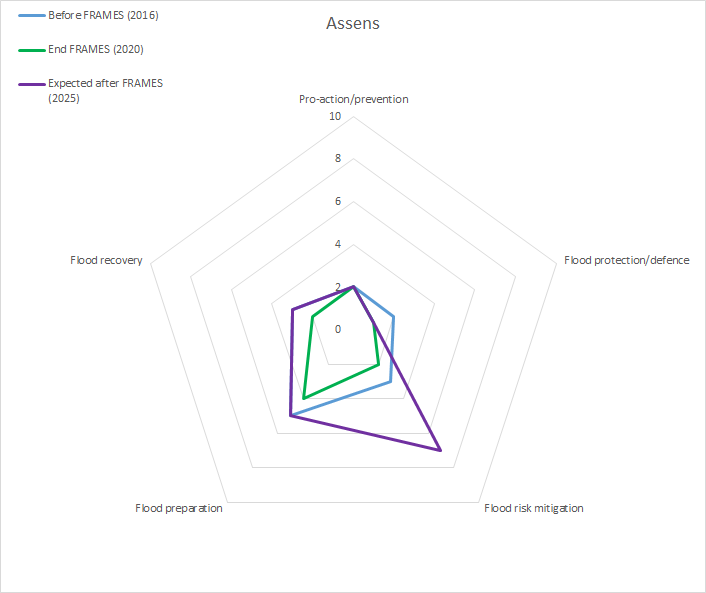
Figure 1: Initial, final and expected scores per layer in this pilot (Transnational Monitor and Evaluation report, 2020)
To measure the impact of FRAMES on improving the flood resilience of pilot areas, communities and authorities both a baseline and final monitoring survey have been conducted. The surveys were completed by pilot managers in consultation with key pilot stakeholders. The baseline survey included questions about the actual situation in 2017 (before the project started) and expectations for 2020 (expectations were not filled out for this particular pilot) (see figure 1). The final survey contained similar questions, but about the actual situation in 2020 and expected situation for 2025, five years after the pilot projects are finished. All the scores for both surveys along with an interpretation, can be found in chapter 8 of the Transnational Monitoring and Evaluation Report.
Stakeholders involved
- Danish Coastal Authority (DCA)
- Representative from the harbor (semi-privately owned)
- Municipality of Assens:
- A project manager in climate adaptation
- City planning
Role of key actors
- Danish Coastal Authority (DCA) is to lead the project activities and had to adjust the DAPP approach to the municipality needs. They developed the Dynamic Measures maps and related explanatory documents together with the municipality. After the project, their role will be to provide guidance on how municipalities can adjust/improve their flood risk management plans according to the EU directive.
- Municipalities: are the key actor for developing the Dynamic measure maps and climate adaptation plan for the city. The municipality has based on the experience from this project applied and received funding for starting a process on establishing a recreational coastal protection measure in one part of the area. Following FRAMES they will continue the work on this project and work towards deciding long term plans for the area.
- Harbor: Key stakeholder for the municipality. Gave valuable input in the process with the practical experience and their vision for the area. They are interested in keeping the harbour activity.
Main activities
Note that the implementation process is the same as in Vejle - the steps were already defined and tested during that pilot, so the difficulties encountered there could be avoided in this pilot.
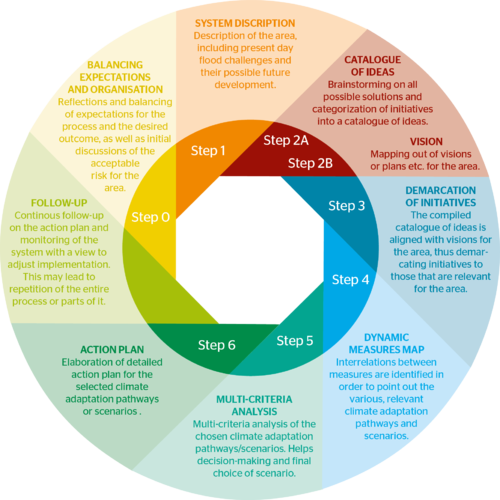
The following steps, visualized in the figure above by DCA, were taken:
Step 0 is about alignment of expectations and is useful for reflections and discussions about the desired outcome of the dynamic planning process. This step should clarify the purpose of the work and ensure that the work group has the mandate required to carry through the task. It is essential to a successful process that suitable resources are available both in terms of time and manpower.
Step 1 is a description of the target area for the planning process and the system, which influences that area. The purpose of this initial step is to create a joint understanding of the area and present day flood challenges, how these challenges may develop in future, as well as the uncertainties involved.
Step 2 consists of two parts. Part one, Step 2A, is a general brainstorming process to come up with ideas of how to handle flood challenges. These ideas are then sorted into relevant categories and organised into a catalogue of ideas. The second part, Step 2B, is an overview of visions, plans ect., already in place for the area, in order to align solutions generated in the course of the process with existing visions and planning.
Step 3 is a revision of Step 2, with a view to demarcate or broaden the possible initiatives compiled the catalogue of ideas in line with visions mapped out. This should ensure weeding out of initiatives that contend with the general development plans for the area.
Step 4 is a compilation and sorting of initiatives. The aim is to find initiatives that match the visions for the town and reduce the risk at the same time. This should demonstrate the interrelation between the various initiatives, as well as their mutual dependencies. This is the platform from which the desired climate adaptation paths are chosen. This step may also be useful in clarifying any general scenarios suitable for communication work or for further discussion at the political level.
Step 5 is a multi-criteria analysis (MCA) for a limited number of selected pathways from the map of measures. At this stage it will be beneficial to include weighting by stakeholders and politicians, since the multi-criteria analysis is a decision-making tool, designed to find the desired climate adaptation pathways for the area.
Step 6 is the elaboration of a detailed action plan for the work with the climate adaptation pathways or scenarios selected based on the completed process and the multi-criteria analysis.
Step 7: follow-up. Once the process is completed, a continous follow-up and monitoring of the system should be initiated. System changes, requirement for a more detailed perspective or new insights gathered along the way may mean that the process will have to be repeated. This will ensure that the plan and it implementation are adjusted, when necessary.